For industry professionals well-versed in the art and science of paper making, the significance of controlling paper color and brightness extends beyond aesthetic appeal—it influences the paper’s functionality and consumer perception. Let’s delve into why rigorous management of these properties is critical for maintaining excellence in paper production.
What is Paper Whiteness and Brightness?
In the paper industry, brightness and whiteness are critical properties that affect both the appearance and performance of paper. Brightness refers to how much blue light a paper reflects, specifically at the wavelength of 457 nm. This is crucial because it interacts with lignin, a natural “glue” in paper that can give it a yellowish tint; hence, a higher brightness value indicates less yellowing and better bleaching of the paper pulp.
Whiteness, on the other hand, measures the relative balance of light reflected across the full visible spectral range (approximately 380 nm – 720 nm). This provides a more comprehensive understanding of the paper’s color quality.
An important metric related to whiteness is the CIE Whiteness index. This single-number index references the relative degree of near-white materials under specific lighting conditions and is the most commonly used whiteness index in the industry.

The Bottom Line When Managing Brightness
Enhanced Product Quality: Controlling brightness and color consistency is key to producing high-quality paper that meets the aesthetic and functional standards demanded by the market. This control directly impacts the paper’s appeal and usability, particularly in color-critical applications like printing and fine art.
Increased Production Efficiency: By consistently monitoring brightness and color, manufacturers can detect variations early in the production process. This early detection allows for quick adjustments, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
Optimized Material Use: Precise brightness measurements help in the optimal application of optical brighteners, which are crucial for achieving the desired whiteness without overuse. This precise application saves costs and ensures the long-term quality of the paper.
How Do We Measure Brightness?
The industry employs several standardized methods to measure paper brightness, ensuring consistency and reliability across different products and batches. Here are a few:
T525 and T452 Standards: These involve measuring the diffuse and directional reflectance of the paper at 457 nm.
ISO 2470 and ISO 2469: These standards focus on measuring the diffuse blue reflectance factor, also known as ISO brightness, and the overall diffuse factor.
Different measurement methods can yield varying results, influenced by the paper’s texture and other properties. Spectrophotometers, like the Datacolor Elrepho 1000, are essential for accurately measuring these properties. This spectrophotometer is designed to support a wide range of industry standards, including ISO, DIN, SCAN, and TAPPI, making it a versatile tool for ensuring precise and reliable quality control in paper production.
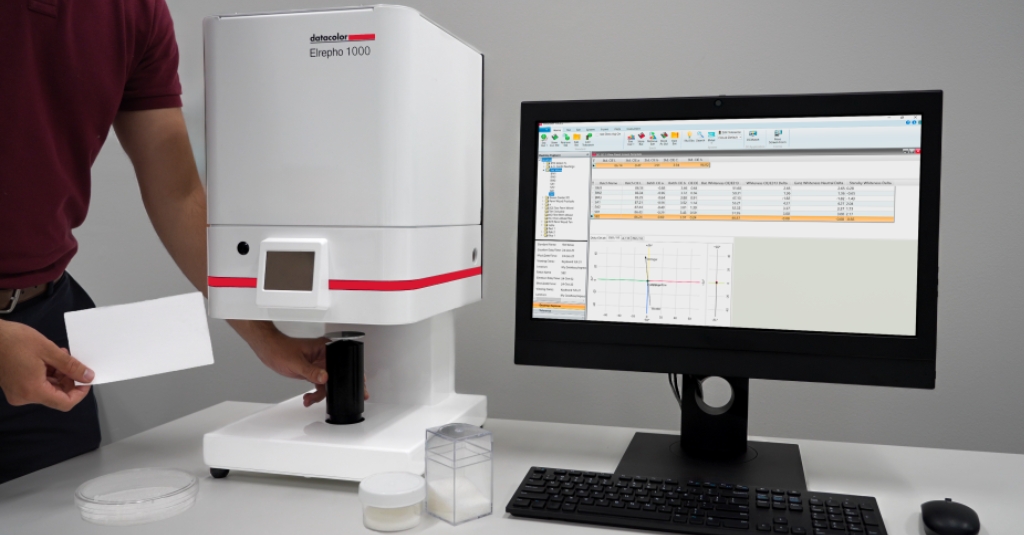

Diffuse vs. Directional Brightness
In diffuse brightness testing, light is scattered uniformly across the paper’s surface, providing a general measure of its reflectance. This method uses an integrating sphere to diffuse the light and a photodetector to measure the brightness. The diffuse illumination is at 0° (d/0°), which is the generally accepted measurement technique in the paper industry as used by the Datacolor Elrepho 1000.
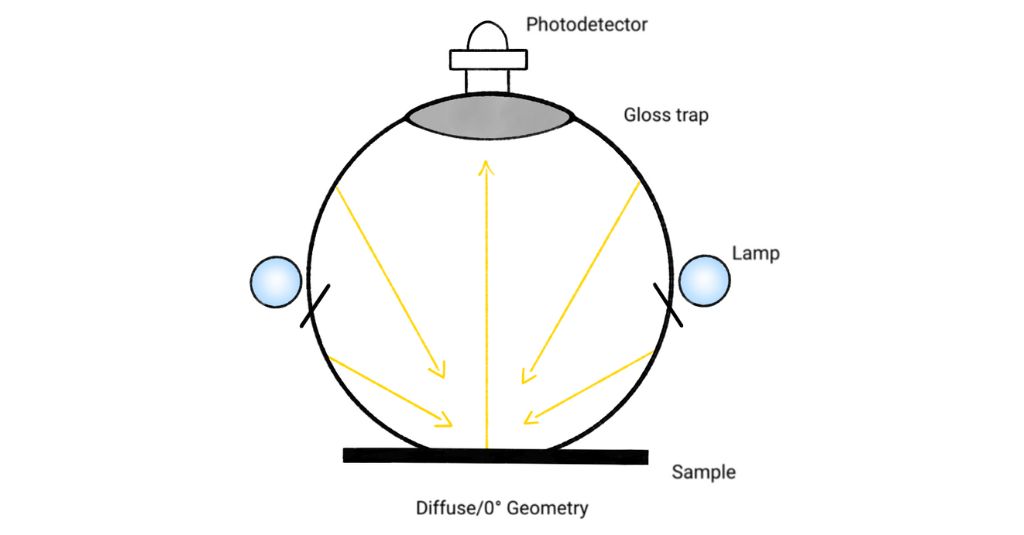
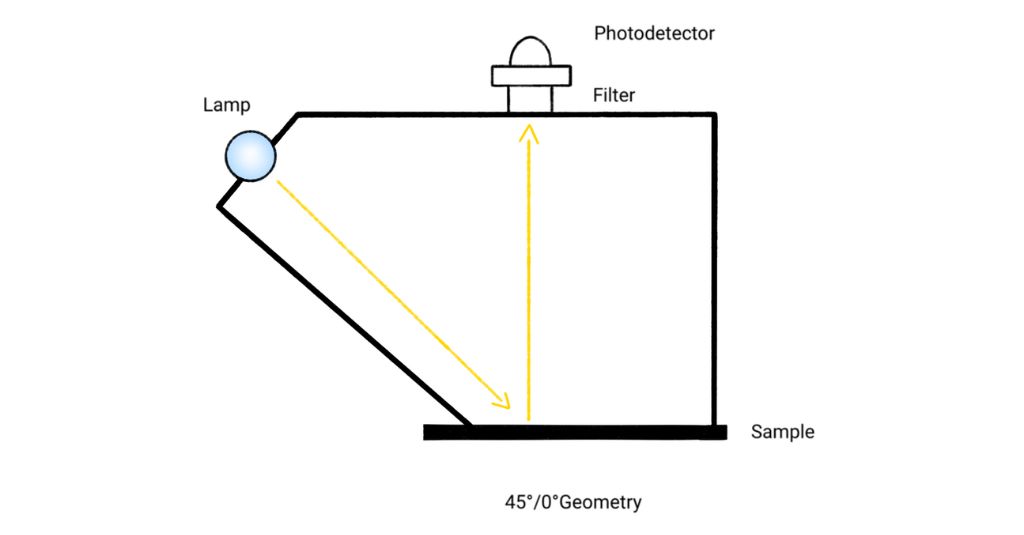
Conversely, directional brightness testing involves a light source angled at 45 degrees to the paper, measuring how light reflects off the paper in a specific direction. This method, known as directional brightness (45°/0°), is less common. Its drawback is that if the sample has any structure, it will affect the color.
The Role of Optical Brighteners
Optical brighteners are chemicals added to paper to enhance its brightness. They work by absorbing ultraviolet light and re-emitting it as visible blue light, thus boosting the paper’s overall brightness. The effectiveness of these brighteners can vary based on the amount of UV light exposure and the specific type of brightener used.
Why Brightness Matters
The brightness of paper affects not only its aesthetic appeal but also its functionality. In the printing industry, for example, brighter paper can lead to sharper and more vibrant print quality. For everyday consumers, brighter paper is often associated with higher quality and cleanliness, influencing purchasing decisions.
Elevating Paper Excellence
Effective management of paper brightness is not just about adhering to standards—it directly enhances the quality and desirability of your paper products. By understanding and controlling these essential attributes, you can ensure your paper not only looks better but also performs better in its intended applications.
Explore the precision of the Datacolor Elrepho 1000 to maintain exceptional quality standards. Interested in optimizing your processes? Contact a Datacolor Color Expert today to learn how this technology can elevate your production.
Want to learn more about Elrepho 1000?
Chat with an Expert!









